Foot problems in diabetes
People with diabetes are prone to foot diseases due to long-term high blood sugar. Diabetic neuropathy and peripheral vascular disease are the two main causes of diabetic foot problems, and both can have serious complications.

Complications of the foot in patients with diabetes
1. What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a disease that causes faulty or insufficient insulin production or low sensitivity to insulin. Insulin is an essential hormone that is responsible for helping cells absorb sugar from the blood to use for energy.
When this process does not work correctly, sugar remains circulating in the blood, causing health problems.
Prolonged periods of high sugar levels in the blood can damage many areas of the body, including the feet.
Diabetes is the cause of more than 50% of all leg amputations in the United States. In this article, we look at foot problems that can occur in people with uncontrolled or poorly managed diabetes and how these effects can be managed.
2. How does diabetes affect the feet?
The two main foot problems that occur in people with diabetes are:
-
Diabetic neuropathy: diabetes can cause nerve damage that leads to numbness in the feet. This can make it hard for people with diabetes to feel sensation in their extremities.The condition also makes it difficult for a person with diabetes to feel irritation, soreness, or infection on the feet. They may not notice when their shoes are rubbing. This lack of sensation can lead to an increased risk of cuts, sores, and blisters.
-
Peripheral vascular disease: Diabetes leads to changes in the blood vessels, including arteries. In peripheral vascular disease, fatty deposits block vessels beyond the brain and heart. Reduced blood flow can lead to pain, infection, and wounds that heal slowly. If a person develops a severe infection, a doctor may recommend amputation.
3. Signs of Diabetic Foot
Diabetic foot symptoms vary from person to person and may depend on the specific problems a person is having at the time.
However, symptoms may include:
-
a loss of feeling
-
numbness or tingling sensation
-
blisters or other wounds without pain
-
skin discoloration and temperature changes
-
red streaks
-
wounds with or without drainage
-
painful tingling
-
staining on socks
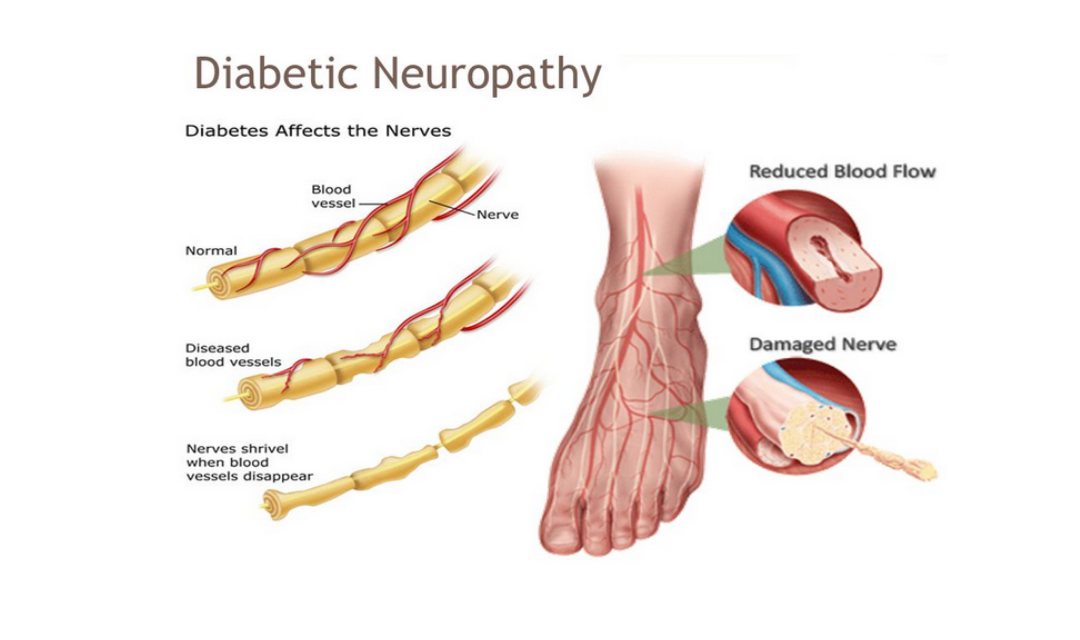
Diabetic neuropathy
4. Treatment for diabetic foot problems
Treatment for diabetic foot problems varies according to the severity of the condition. A range of surgical and nonsurgical options is available.

Diabetic foot after treatment with Multidex
In a nutshell, foot problems in diabetes can occur due to restricted blood flow and unnoticed cuts and infections that develop due to numbness in the area. A person with diabetes needs regular podiatric checks to ensure that any foot problems do not develop into complications.