Why does diabetes cause leg ulcers?
Foot ulcers are a common complication of diabetes that is not being managed through methods such as diet, exercise, and insulin treatment. Ulcers are formed as a result of skin tissue breaking down and exposing the layers underneath.They’re most common under your big toes and the balls of your feet, and they can affect your feet down to the bones. Treatment for diabetic foot ulcers varies depending on their causes.
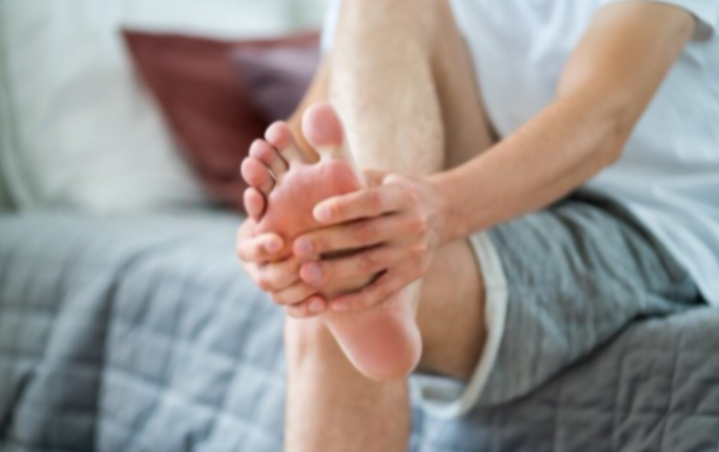

Leg ulcers are most common under the big toe and in the metatarsal region and can affect the bones of the foot
1. Identifying symptoms
One of the first signs of a foot ulcer is drainage from your foot that might stain your socks or leak out in your shoe. Unusual swelling, irritation, redness, and odors from one or both feet are also common early symptoms.
The most visible sign of a serious foot ulcer is black tissue (called eschar) surrounding the ulcer. This forms because of an absence of healthy blood flow to the area around the ulcer.
Partial or complete gangrene, which refers to tissue death due to infections, can appear around the ulcer. In this case, odorous discharge, pain, and numbness can occur. Signs of foot ulcers are not always obvious. Sometimes, you won’t even show symptoms of ulcers until the ulcer has become infected.
2. Ulcer Classification System
Your doctor will likely identify the seriousness of your ulcer on a scale of 0 to 5 using the Wagner Ulcer Classification System:
0: no open lesions; may have healed lesion
1: superficial ulcer without penetration to deeper layers
2: deeper ulcer, reaching tendon, bone, or joint capsule
3: deeper tissues involved, with abscess, osteomyelitis, or tendonitis
4: gangrene in a portion of forefoot or heel
5: extensive gangrenous involvement of the entire foot
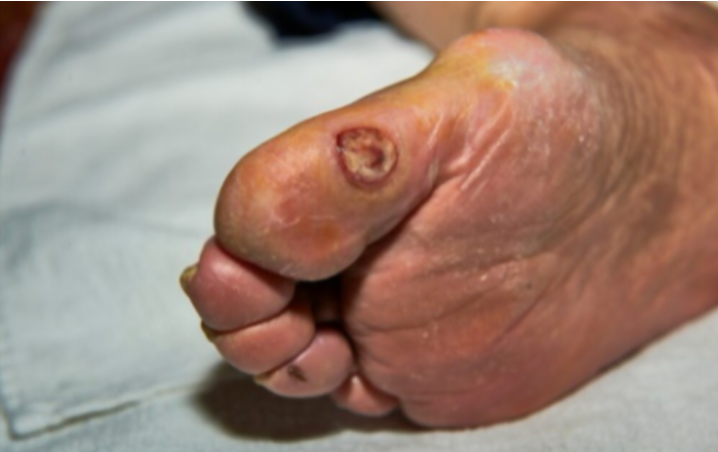
Multidex is effective in the treatment of severe diabetic foot ulcers
3. Causes of diabetic foot ulcers
Ulcers in people with diabetes are most commonly caused by:
- Poor circulation: is a form of vascular disease in which blood doesn’t flow to your feet efficiently. Poor circulation can also make it more difficult for ulcers to heal.
- High blood sugar (hyperglycemia): can slow the healing process of an infected foot ulcer, so blood sugar management is critical. People with type 2 diabetes and other ailments often have a harder time fighting off infections from ulcers.
- Nerve damage: Nerve damage is a long-term effect and can lead to a loss of feeling in your feet. Damaged nerves can feel tingly and painful. Nerve damage reduces sensitivity to foot pain and results in painless wounds that can cause ulcers.
- Irritated or wounded feet
All people with diabetes are at risk for foot ulcers, which can have multiple causes. Some factors can increase the risk of foot ulcers, including:
- Poorly fitted or poor quality shoes
- Poor hygiene (not washing regularly or thoroughly or not drying the feet well after washing)
- Improper trimming of toenails
- Alcohol consumption
- Eye disease from diabetes
- Heart disease
- Kidney disease
- Obesity
- Tobacco use (inhibits blood circulation)
- Diabetic foot ulcers are also most common in older men.
Multidex contains the main active ingredients maltodextrin and ascorbic acid which have been shown to be remarkably effective in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. In a study published in the Journal of Tissue Viability in 2017, the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers with maltodextrin/ascorbic acid demonstrated nearly four times greater wound closure than zinc oxide.
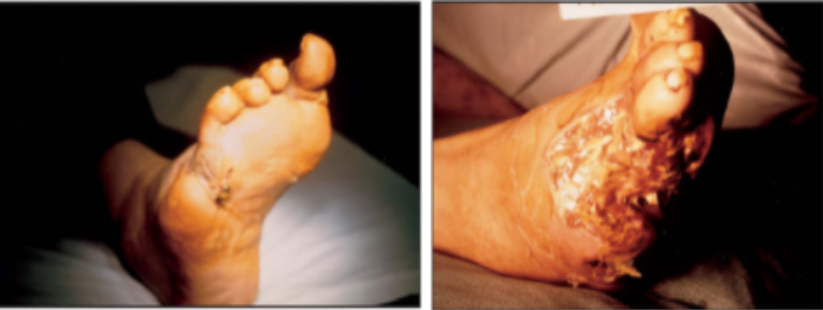
Pictures of diabetic feet after and before 1 month of treatment with Multidex
When caught early, foot ulcers are treatable. See a doctor right away if you develop a sore on your foot, as the likelihood of infection increases the longer you wait. Untreated infections may require amputations. While your ulcers heal, stay off your feet and follow your treatment plan. Diabetic foot ulcers can take several weeks to heal.